HarmonyOS
HarmonyOS Feature: App Guard – System Security

HarmonyOS comes with lots of new features including the latest App Guard, system security. This new addition allows you to safeguard your smartphone from unknown security threats from any apps that could harm your smartphone.
According to the information, apps on AppGallery are verified as safe, having passed rigorous security checks. Once the App Guard is enabled, the system will recommend that you download apps through Huawei AppGallery, whenever is possible, to protect your device and data from risky apps.
If you have this app enabled, you’ll get a warning regarding the app that you are proceeding to install.
How to enable HarmonyOS App Guard:
AppGuard is enabled by default but you can check it up from the system settings.
- Open Settings
- System & updates
- App Guard
- Disable
Swipe down from the upper-right edge of the screen to display Control Panel, touch, select Edit switches, drag App Guard to the shortcut switches panel, and enable the feature.
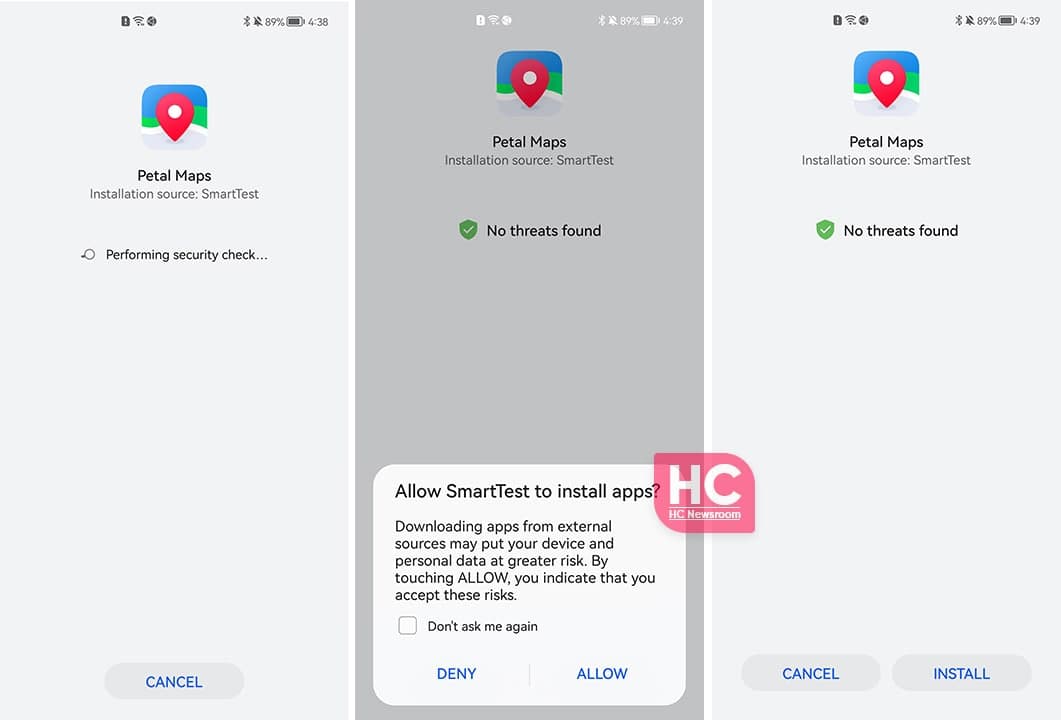
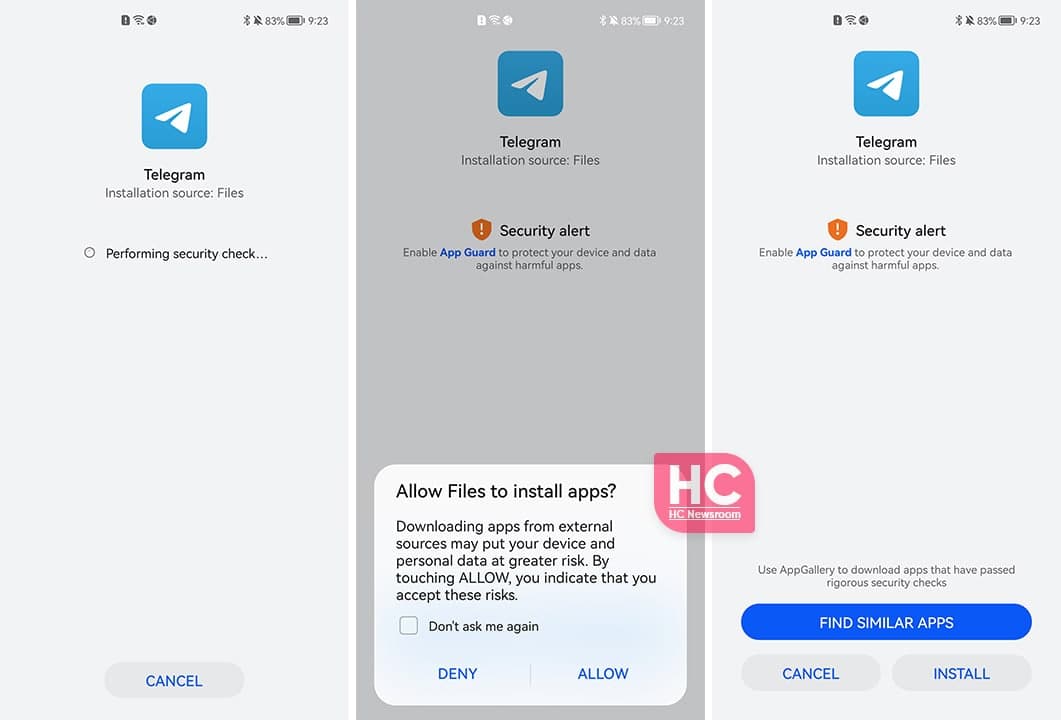
When installing apps from sources other than Huawei AppGallery:
If the app is available in Huawei AppGallery, follow the onscreen instructions to install it via Huawei AppGallery or touch Install anyway to proceed to install it from the current source.
If the app is not available in AppGallery, you are not advised to install it. If you trust the app, you can follow the onscreen instructions to touch Install anyway and enter your password to complete the installation. If the system detects that the app involves uncontrollable risks, you will not be allowed to install the app.
App Guard:
App Guard is a system feature intended to ensure the security of apps and services. After App Guard is
enabled, you will be advised to download apps via Huawei AppGallery if possible, as all apps have
to undergo the following four-layer precautions before being released in AppGallery:
- Malicious behavior detection: To detect viruses, Trojan horses, worms, malicious fee deductions, and malicious data consumption.
- Security vulnerability scanning: To ensure component security, password input security, and command execution security.
- Privacy leakage check: To prevent authorization of unnecessary data access, personal data leakage, and lack of a privacy statement.
- Manual real-name authentication: To ensure security by performing the test on a real device with a real person in real scenarios.






