Wearables
Huawei confirms Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia) feature for Watch 4 series

Huawei has officially confirmed Hyperglycemia AKA high blood sugar assessment feature for the upcoming Huawei Watch 4 series. This is a major breakthrough as the new smart wearable lineup will unveil on May 18th in China.
The latest announcement is coming directly from the Huawei Consumer Business Group CEO, Yu Chengdong. He confirmed that Huawei Watch 4 series will equip with high blood sugar risk assessment technology. This is the latest innovation and a win for Huawei as a leader in smartwatch technologies.
Hyperglycemia:
Hyperglycemia is the technical term for high blood glucose (blood sugar). High blood glucose happens when the body has too little insulin or when the body can’t use insulin properly.
Research:
“I am very happy to share with you one of our latest achievements in the field of health,” wrote Mr. Yu.
Since 2013, the Huawei Health project is continuously working with authoritative medical institutions. And Huawei has made new progress in the field of blood sugar health. Anyone can join the research project and can experience the latest smartwatch with a high blood sugar assessment feature.
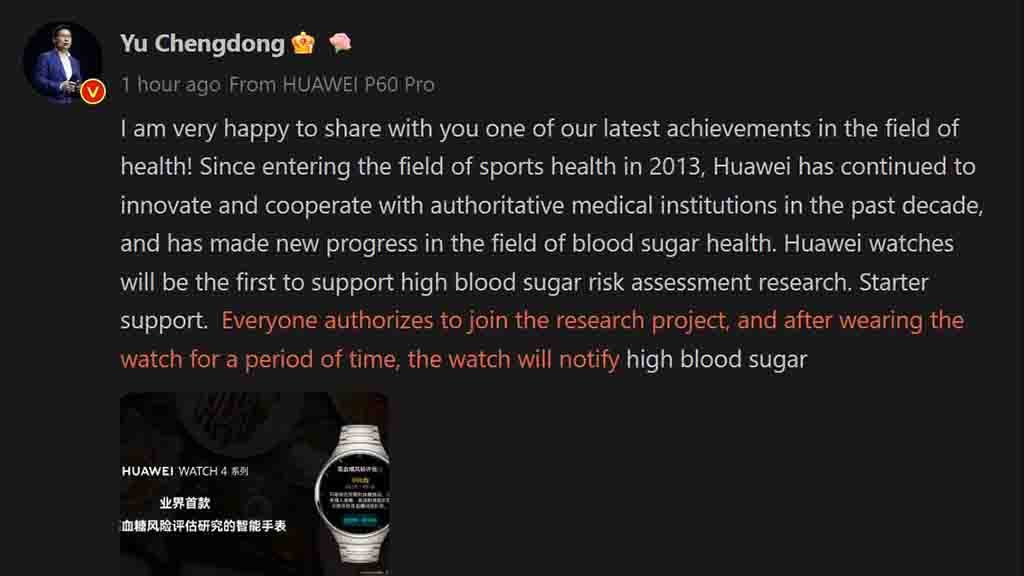
Information on this matter revealed that the high blood sugar risk assessment study supported by the Huawei Watch 4 series is based on the analysis of 100,000+ hours of monitoring and 800,000+ pieces of blood sugar data.
This data standard includes aspects of monitoring including heart rate, pulse wave characteristics, and more. These have self-similarity and helped in creating a hyperglycemia analysis algorithm to assess the risk of hyperglycemia.
“Huawei hopes to use smarter products and more professional health research to help everyone maintain the first line of defense in health.” Mr. Yu Concluded.
Current details:
According to the image shared by Huawei CEO, this product is not a medical device, and the measurement data and results are for reference only, not as a basis for diagnosis and treatment. This is a common advisory note for all of the health-related smartwatches in promotions.
Moving on, this feature requires users to join the blood sugar health research initiated by a third-party professional medical institution. The program is not allowed for users under the age of 18, type I diabetes, gestational diabetes, and other special types of diabetes.
The watch result UI includes the feature name “hyperglycemia risk assessment”. Then there is the label of risk level such as “medium risk. Below, you will find the sign of the risk including:
- Short-term blood sugar fluctuations
The watch also suggests what not to do at this risk level, such as “excessive intake of high-sugar high-oil and high-fat diets may lead to increased risk of high blood sugar”.
The user always has the option to restart a new assessment with the “Start a new round of evaluation” button on the bottom.

Assessment:
As you can see, Huawei will collect the user data for a duration to provide an assessment of the current blood sugar health. This will be a new non-invasive way of providing the details and it’s majorly dependent on the hardware and software technologies.
Apple is far behind:
This will make Huawei Watch 4 series the first smartwatch to come with a blood sugar monitoring feature. Meanwhile, Apple is also developing blood sugar measurement technology but it’s lagging behind. Furthermore, we’ve not seen any related announcements coming from the US tech maker. Past reports suggest this it may take several years for Apple to do so.
Read more – 5 Years ahead of Apple, new Huawei Watch to bring non-invasive blood sugar monitoring
For China only:
Last week, Huawei released Watch 4 series for global consumers but the company has not announced this feature. This means the company is keeping this feature limited to the Chinese market for the time being.
Because the company is currently in the research phase and will take user feedback to improve the Huawei Watch 4 series for better blood sugar assessment feature. Therefore, limited availability is understandable.
(Source)






